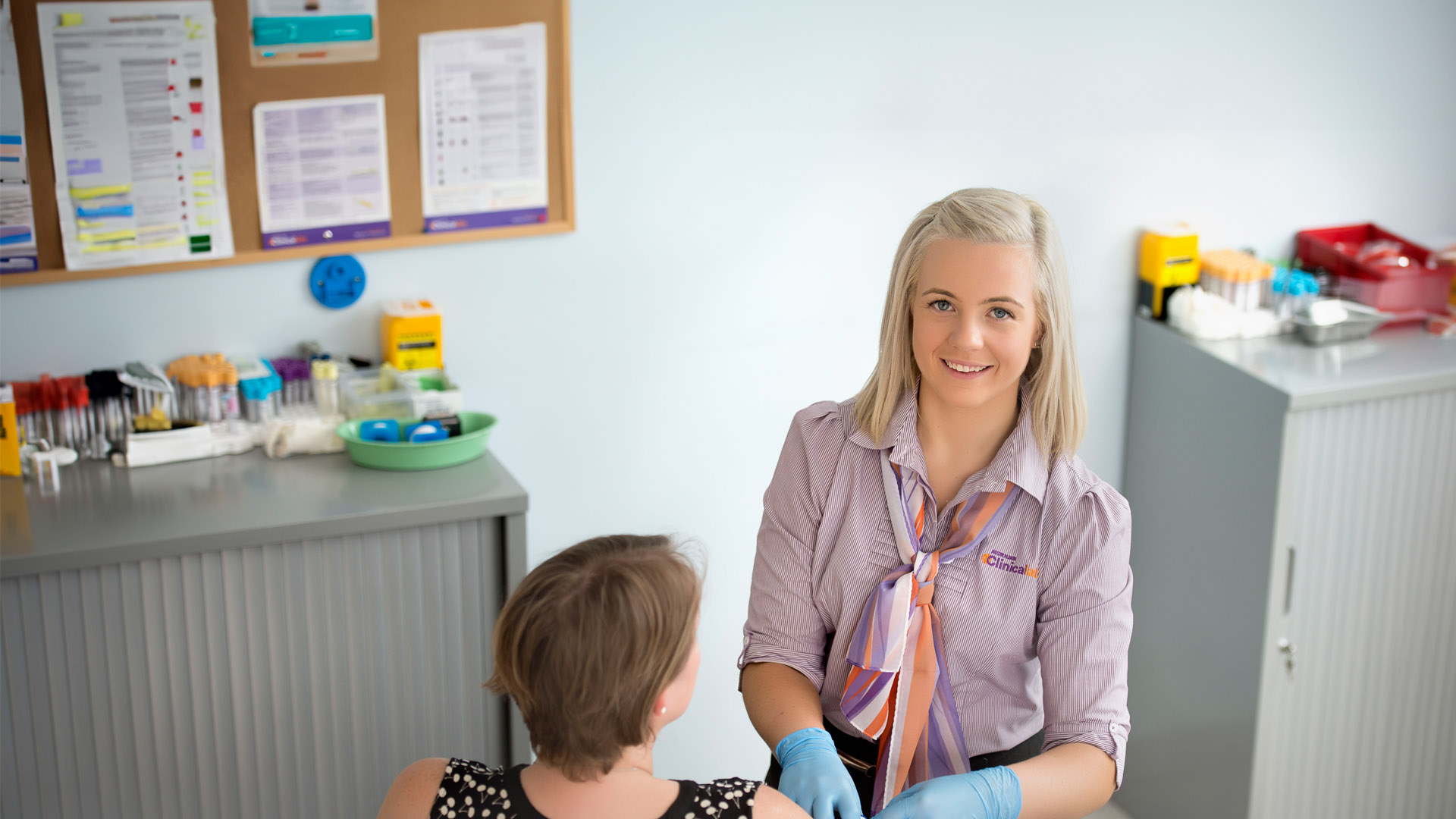
Diabetes is a chronic health condition where the blood glucose levels are too high. The body is unable to make adequate insulin or is not effectively using the insulin produced. Over time, high blood sugar levels can lead to long term health problems such as damage to blood vessels and nerves, which can affect the heart, kidney, eye and foot.
There are three main types of diabetes:
- Type 1 – An autoimmune disease where the immune system attacks and destroys the insulin producing cells in the pancreas, resulting in a lack of insulin production. It is considered lifelong, as there is currently no cure and is not linked to modifiable lifestyle factors.
- Type 2 – A metabolic disorder characterised by insufficient insulin production on a background of insulin resistance. Lifestyle changes such as exercise and healthy diet may help slow or stop the progression of this disease. Pre-diabetes may be diagnosed before it progresses to Type 2 diabetes.
- Gestational diabetes – When blood sugar levels are higher than normal during pregnancy, which can cause the risk of developing complications during pregnancy. All pregnant women should be tested for gestational diabetes at 24-28 weeks of pregnancy and earlier testing is recommended for those with risk factors.